Top 6 Reasons Why Your New Smartphone Still Drops Calls
Powerful Signal answers your questions about cellular connections

Updated
Upgrading to a new smartphone is fun and exciting, something many people enjoy every few years.
What’s not fun or exciting is when your new phone drops calls or won’t sent text messages. Why does this happen? And is there anything that can be done to improve your phone’s reception?
We all understand that if you are in the middle of nowhere, with no cell towers nearby, that you many not have enough signal to make a call. But what if you’re in an urban area with cell towers all around you? Even with local cell service, six main factors may cause cellular reception problems.
Signal strength
Of course, signal strength is the key factor with dropped calls. Cell phones require a minimum cell signal strength to maintain a connection with the cell tower. Signal strength below a minimum threshold—usually less than −120 to −125 dBm—will result in a drop calls, undelivered SMS messages, and little to no internet data.
Carrier frequency
One little-known fact is that the cellular frequency used by your carrier may be the cause of dropped calls in certain locations.
A friend could be standing next to you, each of you with the same smartphone, with one of you on Verizon and the other using AT&T: Your friend may be talking with no problems, while you’re dropping calls. That’s because Verizon and AT&T use different frequencies, and the strength of your cell signal in that spot is different than your friend’s.
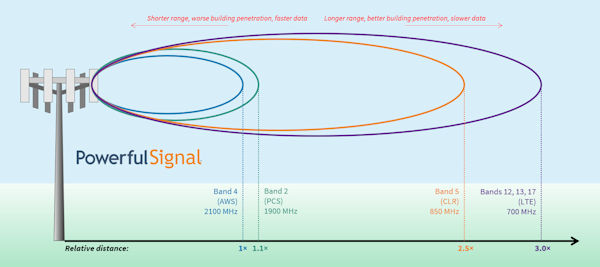
There are five main bands of frequency (along with several others that are becoming more widespread) used in cellular communications:
- Lower 700 MHz LTE-A (699–746 MHz)
- Upper 700 MHz LTE-V (746–787 MHz)
- Cellular 850 (824–894 MHz; this is the earliest cellular frequency still in use)
- PCS 1900 (1850–1990 MHz)
- AWS 1700/2100 MHz (1710–1755/2110–2155 MHz)
The higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength. Higher frequencies with shorter wavelengths (PCS and AWS) have faster data speeds, but they travel shorter distances and have more difficulty penetrating building walls. Lower frequencies with longer wavelengths (LTE and Cellular 850) have slower data speeds, but they travel longer distances and more easily penetrate building walls. Given the same cell signal strength and power levels, a 700 MHz LTE signal will travel through open air about three times the distance of a 2100 MHz AWS signal.
Building materials
Dense or reflective building materials block cellular frequencies and cause cell phone reception problems. If you’re inside a building made of these materials, you’re more likely to have inadequate cell signal:
- Concrete
- Steel
- Stone
- Large logs and timbers
- Low-e glass and other types of glass tinting and films
- Metal roofs
- Some types of stucco
Cell phone cases
The premium case you bought to protect your smartphone could be the cause of your cell signal reception problems.
Avoid using cell phone cases with metal components—wrapping your cell phone in metal can create a mini Faraday cage that blocks reception.
Shadowed areas
You’re probably aware of “dead zones” in places where you travel frequently, spots where you’re likely to lose cell phone reception. You may have even warned friends or family members while you’re driving, “I’m coming up to a spot where I’ve got no reception; I’ll call you back in a few minutes.”
Most likely these areas are shadowed by something like a building, a hill, or an underpass. Areas where cell signals are blocked and shadowed can exist anywhere—in cities and suburbs, in rural communities, along major highways and back roads.
User load on cell phone towers
Another little-known fact is that antennas on cell phone towers have limited numbers of simultaneous users they can support. Sometimes cell towers get overloaded—calls in progress will drop and users can’t make new calls.
User load problems often occur during rush hour, traffic jams, and unexpectedly large gatherings of people in one area.
There are solutions to dropped calls!

Cellular networks are getting wider, stronger, and faster, but there will always be gaps in cellular coverage that result in irritating cell signal reception issues.
You don’t have to just put up with poor cell signal reception until your carrier fixes the problem, though. Call Powerful Signal at 435-634-6800 or browse our selection of cell signal boosters for homes, vehicles, and office buildings.
A cell signal booster system can fix your cell phone connection problems. Powerful Signal can find your solution for dropped calls and help keep you connected!